単純な一つの閉ループによるポリゴンの塗りつぶしは
Graphics#FillPolygon(Brush brush, PointF[] pnts)で済む。
マルチポリゴン(穴あきポリゴン)の場合には GraphicsPath を使う。 最初にouter polygon のノード座標値列データ配列をGraphicsPath に登録する。 引き続き inner polygon の座標値列データ配列をGraphicsPath に登録する。 全ての inner polygon について登録が終わったところで、
Graphics#FillPath(Brush brush, GraphicsPath gp)を実行すればよい。
もちろん、単純なポリゴンの塗りつぶしを GraphicsPath を使って行うこともできる。 PointF[] pnts を一つ登録して Graphics#FillPathを実行すればよい。
下に地図アプリでのマルチポリゴンの塗りつぶしプログラムを示す。 GetPointArray では地図システム特有の座標変換を行っている。
public void FillPolygon(Graphics g, Brush br, TileToRender tile) {
int INC = (slim ? 1 : 2);
if (type == 3) {
using (var gp = new GraphicsPath()) {
int off = 0;
for (int n = 0; n < num_polys; n++) {
int length = buff[pos+ixMulti+n]; // ノード数
PointF[] pnts = GetPointArray(tile, off, length);
gp.AddPolygon(pnts);
off += length * INC;
}
g.FillPath(br, gp);
}
} else { // type == 2
PointF[] pnts = GetPointArray(tile, 0, num_nodes);
if (pnts != null) g.FillPolygon(br, pnts);
pnts = null; // GCが速く行われるようだ
}
}
PointF[] GetPointArray(TileToRender tile, int offset, int length) {
if (length < 0) return null;
PointF[] pa = new PointF[length];
double fact = tile.fact;
double xpx = tile.xpx;
double ypx = tile.ypx;
int INC = (slim ? 1 : 2);
int bgn = pos + ixData + offset;
int end = bgn + INC * length;
int k = 0;
for (int ix = bgn; ix < end; ) {
float fx, fy;
if (slim) {
int xy = buff[ix++];
fx = (float) ((x0 + (short)(xy>>16)) * fact - xpx);
fy = (float) ((y0 + (short)(xy&0xffff)) * fact - ypx);
} else {
fx = (float) (buff[ix++] * fact - xpx);
fy = (float) (buff[ix++] * fact - ypx);
}
pa[k++] = new PointF(fx, fy);
}
return pa;
}
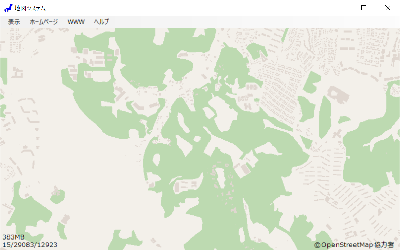
下図で、ほぼ中央に大きな outer polygon(森林)があり、その中には多くの inner polygon がある。 それらを除外して outer polygon が描画されている。
