エリアのアイコンや名称はその中心に描画する。 凸多角形の場合、全ノードの平均座標値をそのポリゴンの中心座標値とすればいいが、 蛇行した川に沿った公園とか、入り組んだ形状のダム(貯水池)の場合、 幾何学的な中心がポリゴンの外になってしまうケースがある。
必ずポリゴン内にある点をなるべく簡単な方法で求めたい。
Mapnik の場合、interior.cpp で算出している。これは mapbox/polylabel を改良したもののようだ。
Windows パソコン/タブレット用の地図システムは C# で作成している。 このため、Androidスマホへの移植では、当初、Xamarin C# に期待をかけていた。
しかし、少し試した段階で、Xamarin C# は Windows C# とは全く別物であることが分かった。 特に、Windows C# でのグラフィクス処理は内部的には GDI+ で実装されている。 Android Studio 上の Xamarin C# では GDI+ はサポートしていない。
Android OS は Windows OS などと比較すると、短期間でバージョンアップを繰り返している。 Android上の Xamarin C# は当然、これに振り回されるため、ネットには現行のバージョンに通用する情報が少ない。
この二つの理由により、Xamarin C# の使用を断念して、パソコンでは純正Java、スマホでは Android Java を 使うことにした。
パソコン上のバイナリレコード作成などはこれまで通り C# でもいいが、 スマホとの親和性から Java に変えることにした。
C# には PriorityQueue が存在しないため、この実装も必要であったが、 Java には PriorityQueue があるため、この点では C# より負担が減少した。
private final static float EPSILON = 1E-7f;
static Cell centroid;
static float max_size;
private static class Cell implements Comparator<Object> {
public float X, Y, H, D, Max;
public Cell() {}
public Cell(float x, float y, float h, float[][][] polygon) {
X = x;
Y = y;
H = h;
D = PointToPolygonDist(X, Y, polygon);
if (centroid != null) {
double dx = X - centroid.X;
double dy = Y - centroid.Y;
double distance_centroid = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (D > 0 && distance_centroid < max_size)
D = (float)(D * (1 - distance_centroid / max_size));
}
Max = D + H * (float)Math.sqrt(2);
}
public int compare(Object obj1, Object obj2) {
Cell cell1 = (Cell)obj1;
Cell cell2 = (Cell)obj2;
float num1 = cell1.Max;
float num2 = cell2.Max;
if(num1 > num2) {
return 1;
} else if(num1 < num2) {
return -1;
} else{
return 0;
}
}
}
//Signed distance from point to polygon outline (negative if point is outside)
static float PointToPolygonDist(float x, float y, float[][][] polygon) {
boolean inside = false;
float minDistSq = Float.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = 0; k < polygon.length; k++) {
float[][] ring = polygon[k];
for (int i = 0, len = ring.length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
float[] a = ring[i];
float[] b = ring[j];
if ((a[1] > y != b[1] > y) && (x < (b[0] - a[0]) * (y - a[1]) / (b[1] - a[1]) + a[0]))
inside = !inside;
minDistSq = Math.min(minDistSq, GetSegDistSq(x, y, a, b));
}
}
return ((inside ? 1 : -1) * (float)Math.sqrt(minDistSq));
}
//Get squared distance from a point to a segment
private static float GetSegDistSq(float px, float py, float[] a, float[] b) {
float x = a[0];
float y = a[1];
float dx = b[0] - x;
float dy = b[1] - y;
if (!FloatEquals(dx, 0) || !FloatEquals(dy, 0)) {
float t = ((px - x) * dx + (py - y) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (t > 1) {
x = b[0];
y = b[1];
} else if (t > 0) {
x += dx * t;
y += dy * t;
}
}
dx = px - x;
dy = py - y;
return (dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
public static long getCenter(long[] poly, int length) {
float[][][] polygon = new float[1][][];
polygon[0] = new float[length][];
for (int n = 0; n < length; n++) {
polygon[0][n] = new float[2];
polygon[0][n][0] = getX(poly[n])/10000000.0f;
polygon[0][n][1] = getY(poly[n])/10000000.0f;
}
Cell centroid = getCentroidCell(polygon);
float[] point = getCenter(polygon, centroid);
int lon = (int)(point[0]*10000000);
int lat = (int)(point[1]*10000000);
return (((long)lon)<<32) | (lat & 0xffffffffL);
}
public static float[] getCenter(float[][][] polygon, Cell centroid) {
//Find the bounding box of the outer ring
float minX = Float.MAX_VALUE, minY = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float maxX = Float.MIN_VALUE, maxY = Float.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon[0].length; i++) {
float[] p = polygon[0][i];
if (p[0] < minX) minX = p[0];
if (p[1] < minY) minY = p[1];
if (p[0] > maxX) maxX = p[0];
if (p[1] > maxY) maxY = p[1];
}
float width = maxX - minX;
float height = maxY - minY;
float cellSize = Math.min(width, height);
float h = cellSize / 2;
max_size = Math.max(width, height);
float precision = cellSize * 3.0f / 100.0f; // 3%. 2021.11.30
//A priority queue of cells in order of their "potential" (max distance to polygon)
Queue<Cell> cellQueue = new PriorityQueue<Cell>(4, new Cell());
if (FloatEquals(cellSize, 0))
return new float[] { minX, minY };
//Take centroid as the first best guess
//centroid = new Cell(centro[0], centro[1], h, polygon);
Cell bestCell = centroid;
//Cover polygon with initial cells
for (double x = minX; x < maxX; x += cellSize) {
for (double y = minY; y < maxY; y += cellSize) {
Cell cell = new Cell((float)(x + h), (float)(y + h), h, polygon);
//cellQueue.enqueue(cell.Max, cell);
cellQueue.add(cell);
}
}
//Special case for rectangular polygons
Cell bboxCell = new Cell(minX + width/2, minY + height/2, 0, polygon);
if (bboxCell.D > bestCell.D)
bestCell = bboxCell;
int numProbes = cellQueue.size();
while (cellQueue.size() > 0) {
//Pick the most promising cell from the queue
//Cell cell = cellQueue.Dequeue();
Cell cell = cellQueue.poll();
//Update the best cell if we found a better one
if (cell.D > bestCell.D) {
bestCell = cell;
}
//Do not drill down further if there's no chance of a better solution
if (cell.Max - bestCell.D <= precision)
continue;
//Split the cell into four cells
h = cell.H / 2;
Cell cell1 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.add(cell1);
Cell cell2 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.add(cell2);
Cell cell3 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.add(cell3);
Cell cell4 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.add(cell4);
numProbes += 4;
}
return (new float[] { bestCell.X, bestCell.Y });
}
//Get polygon centroid
private static Cell getCentroidCell(float[][][] polygon) {
float area = 0, x = 0, y = 0;
float[][] ring = polygon[0];
for (int i = 0, len = ring.length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
float[] a = ring[i];
float[] b = ring[j];
float f = a[0] * b[1] - b[0] * a[1];
x += (a[0] + b[0]) * f;
y += (a[1] + b[1]) * f;
area += f * 2;
}
if (FloatEquals(area, 0))
return (new Cell(ring[0][0], ring[0][1], 0, polygon));
return (new Cell(x/area, y/area, 0, polygon));
}
static boolean FloatEquals(float a, float b) {
return (Math.abs(a - b) < EPSILON);
}
public static boolean PointInPolygon(long p, long[] poly) {
boolean inside = false;
long p1, p2, oldPoint = poly[poly.length-1];
for (int i = 0; i < poly.length; i++) {
long newPoint = poly[i];
if (getX(newPoint) > getX(oldPoint)) { p1 = oldPoint; p2 = newPoint; }
else { p1 = newPoint; p2 = oldPoint; }
if ( ( (getX(p1) < getX(p)) == (getX(p) <= getX(p2)) ) &&
( (double)(getY(p) - getY(p1)) * (getX(p2) - getX(p1)) <
(double)(getY(p2) - getY(p1)) * (getX(p) - getX(p1)) ) ) {
inside = !inside;
}
oldPoint = newPoint;
}
return inside;
}
'use strict';
var Queue = require('tinyqueue');
if (Queue.default) Queue = Queue.default; // temporary webpack fix
module.exports = polylabel;
module.exports.default = polylabel;
function polylabel(polygon, precision, debug) {
precision = precision || 1.0;
// find the bounding box of the outer ring
var minX, minY, maxX, maxY;
for (var i = 0; i < polygon[0].length; i++) {
var p = polygon[0][i];
if (!i || p[0] < minX) minX = p[0];
if (!i || p[1] < minY) minY = p[1];
if (!i || p[0] > maxX) maxX = p[0];
if (!i || p[1] > maxY) maxY = p[1];
}
var width = maxX - minX;
var height = maxY - minY;
var cellSize = Math.min(width, height);
var h = cellSize / 2;
if (cellSize === 0) {
var degeneratePoleOfInaccessibility = [minX, minY];
degeneratePoleOfInaccessibility.distance = 0;
return degeneratePoleOfInaccessibility;
}
// a priority queue of cells in order of their "potential" (max distance to polygon)
var cellQueue = new Queue(undefined, compareMax);
// cover polygon with initial cells
for (var x = minX; x < maxX; x += cellSize) {
for (var y = minY; y < maxY; y += cellSize) {
cellQueue.push(new Cell(x + h, y + h, h, polygon));
}
}
// take centroid as the first best guess
var bestCell = getCentroidCell(polygon);
// second guess: bounding box centroid
var bboxCell = new Cell(minX + width / 2, minY + height / 2, 0, polygon);
if (bboxCell.d > bestCell.d) bestCell = bboxCell;
var numProbes = cellQueue.length;
while (cellQueue.length) {
// pick the most promising cell from the queue
var cell = cellQueue.pop();
// update the best cell if we found a better one
if (cell.d > bestCell.d) {
bestCell = cell;
if (debug) console.log('found best %f after %d probes', Math.round(1e4 * cell.d) / 1e4, numProbes);
}
// do not drill down further if there's no chance of a better solution
if (cell.max - bestCell.d <= precision) continue;
// split the cell into four cells
h = cell.h / 2;
cellQueue.push(new Cell(cell.x - h, cell.y - h, h, polygon));
cellQueue.push(new Cell(cell.x + h, cell.y - h, h, polygon));
cellQueue.push(new Cell(cell.x - h, cell.y + h, h, polygon));
cellQueue.push(new Cell(cell.x + h, cell.y + h, h, polygon));
numProbes += 4;
}
if (debug) {
console.log('num probes: ' + numProbes);
console.log('best distance: ' + bestCell.d);
}
var poleOfInaccessibility = [bestCell.x, bestCell.y];
poleOfInaccessibility.distance = bestCell.d;
return poleOfInaccessibility;
}
function compareMax(a, b) {
return b.max - a.max;
}
function Cell(x, y, h, polygon) {
this.x = x; // cell center x
this.y = y; // cell center y
this.h = h; // half the cell size
this.d = pointToPolygonDist(x, y, polygon); // distance from cell center to polygon
this.max = this.d + this.h * Math.SQRT2; // max distance to polygon within a cell
}
// signed distance from point to polygon outline (negative if point is outside)
function pointToPolygonDist(x, y, polygon) {
var inside = false;
var minDistSq = Infinity;
for (var k = 0; k < polygon.length; k++) {
var ring = polygon[k];
for (var i = 0, len = ring.length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
var a = ring[i];
var b = ring[j];
if ((a[1] > y !== b[1] > y) &&
(x < (b[0] - a[0]) * (y - a[1]) / (b[1] - a[1]) + a[0])) inside = !inside;
minDistSq = Math.min(minDistSq, getSegDistSq(x, y, a, b));
}
}
return minDistSq === 0 ? 0 : (inside ? 1 : -1) * Math.sqrt(minDistSq);
}
// get polygon centroid
function getCentroidCell(polygon) {
var area = 0;
var x = 0;
var y = 0;
var points = polygon[0];
for (var i = 0, len = points.length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
var a = points[i];
var b = points[j];
var f = a[0] * b[1] - b[0] * a[1];
x += (a[0] + b[0]) * f;
y += (a[1] + b[1]) * f;
area += f * 3; // f * 2 では?
}
if (area === 0) return new Cell(points[0][0], points[0][1], 0, polygon);
return new Cell(x / area, y / area, 0, polygon);
}
// get squared distance from a point to a segment
function getSegDistSq(px, py, a, b) {
var x = a[0];
var y = a[1];
var dx = b[0] - x;
var dy = b[1] - y;
if (dx !== 0 || dy !== 0) {
var t = ((px - x) * dx + (py - y) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (t > 1) {
x = b[0];
y = b[1];
} else if (t > 0) {
x += dx * t;
y += dy * t;
}
}
dx = px - x;
dy = py - y;
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
}
/*****************************************************************************
*
* This file is part of Mapnik (c++ mapping toolkit)
*
* Copyright (C) 2021 Artem Pavlenko
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*
*****************************************************************************/
#include <mapnik/geometry/interior.hpp>
#include <mapnik/geometry_envelope.hpp>
#include <mapnik/box2d.hpp>
#include <mapnik/geometry_centroid.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#include <mapnik/warning_ignore.hpp>
#include <boost/optional.hpp>
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
namespace mapnik { namespace geometry {
// Interior algorithm is realized as a modification of Polylabel algorithm
// from https://github.com/mapbox/polylabel.
// The modification aims to improve visual output by prefering
// placements closer to centroid.
namespace detail {
// get squared distance from a point to a segment
template <class T>
T segment_dist_sq(const point<T>& p,
const point<T>& a,
const point<T>& b)
{
auto x = a.x;
auto y = a.y;
auto dx = b.x - x;
auto dy = b.y - y;
if (dx != 0 || dy != 0) {
auto t = ((p.x - x) * dx + (p.y - y) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (t > 1) {
x = b.x;
y = b.y;
} else if (t > 0) {
x += dx * t;
y += dy * t;
}
}
dx = p.x - x;
dy = p.y - y;
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
}
template <class T>
void point_to_ring_dist(point<T> const& point, linear_ring<T> const& ring,
bool & inside, double & min_dist_sq)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0, len = ring.size(), j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++)
{
const auto& a = ring[i];
const auto& b = ring[j];
if ((a.y > point.y) != (b.y > point.y) &&
(point.x < (b.x - a.x) * (point.y - a.y) / (b.y - a.y) + a.x)) inside = !inside;
min_dist_sq = std::min(min_dist_sq, segment_dist_sq(point, a, b));
}
}
// signed distance from point to polygon outline (negative if point is outside)
template <class T>
double point_to_polygon_dist(const point<T>& point, const polygon<T>& polygon)
{
bool inside = false;
double min_dist_sq = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
point_to_ring_dist(point, polygon.exterior_ring, inside, min_dist_sq);
for (const auto& ring : polygon.interior_rings)
{
point_to_ring_dist(point, ring, inside, min_dist_sq);
}
return (inside ? 1 : -1) * std::sqrt(min_dist_sq);
}
template <class T>
struct fitness_functor
{
fitness_functor(point<T> const& centroid, point<T> const& polygon_size)
: centroid(centroid),
max_size(std::max(polygon_size.x, polygon_size.y))
{}
T operator()(point<T> const& cell_center, T distance_polygon) const
{
if (distance_polygon <= 0)
{
return distance_polygon;
}
point<T> d(cell_center.x - centroid.x, cell_center.y - centroid.y);
double distance_centroid = std::sqrt(d.x * d.x + d.y * d.y);
return distance_polygon * (1 - distance_centroid / max_size);
}
point<T> centroid;
T max_size;
};
template <class T>
struct cell
{
template <class FitnessFunc>
cell(const point<T>& c_, T h_,
const polygon<T>& polygon,
const FitnessFunc& ff)
: c(c_),
h(h_),
d(point_to_polygon_dist(c, polygon)),
fitness(ff(c, d)),
max_fitness(ff(c, d + h * std::sqrt(2)))
{}
point<T> c; // cell center
T h; // half the cell size
T d; // distance from cell center to polygon
T fitness; // fitness of the cell center
T max_fitness; // a "potential" of the cell calculated from max distance to polygon within the cell
};
template <class T>
point<T> polylabel(polygon<T> const& polygon, box2d<T> const& bbox , T precision = 1)
{
const point<T> size { bbox.width(), bbox.height() };
const T cell_size = std::min(size.x, size.y);
T h = cell_size / 2;
// a priority queue of cells in order of their "potential" (max distance to polygon)
auto compare_func = [] (const cell<T>& a, const cell<T>& b)
{
return a.max_fitness < b.max_fitness;
};
using Queue = std::priority_queue<cell<T>, std::vector<cell<T>>, decltype(compare_func)>;
Queue queue(compare_func);
if (cell_size == 0)
{
return { bbox.minx(), bbox.miny() };
}
point<T> centroid;
if (!mapnik::geometry::centroid(polygon, centroid))
{
auto center = bbox.center();
return { center.x, center.y };
}
fitness_functor<T> fitness_func(centroid, size);
// cover polygon with initial cells
for (T x = bbox.minx(); x < bbox.maxx(); x += cell_size)
{
for (T y = bbox.miny(); y < bbox.maxy(); y += cell_size)
{
queue.push(cell<T>({x + h, y + h}, h, polygon, fitness_func));
}
}
// take centroid as the first best guess
auto best_cell = cell<T>(centroid, 0, polygon, fitness_func);
while (!queue.empty())
{
// pick the most promising cell from the queue
auto current_cell = queue.top();
queue.pop();
// update the best cell if we found a better one
if (current_cell.fitness > best_cell.fitness)
{
best_cell = current_cell;
}
// do not drill down further if there's no chance of a better solution
if (current_cell.max_fitness - best_cell.fitness <= precision) continue;
// split the cell into four cells
h = current_cell.h / 2;
queue.push(cell<T>({current_cell.c.x - h, current_cell.c.y - h}, h, polygon, fitness_func));
queue.push(cell<T>({current_cell.c.x + h, current_cell.c.y - h}, h, polygon, fitness_func));
queue.push(cell<T>({current_cell.c.x - h, current_cell.c.y + h}, h, polygon, fitness_func));
queue.push(cell<T>({current_cell.c.x + h, current_cell.c.y + h}, h, polygon, fitness_func));
}
return best_cell.c;
}
} // namespace detail
template <class T>
bool interior(polygon<T> const& polygon, double scale_factor, point<T> & pt)
{
if (polygon.exterior_ring.empty())
{
return false;
}
const box2d<T> bbox = envelope(polygon.exterior_ring);
// Let the precision be 1% of the polygon size to be independent to map scale.
double precision = (std::max(bbox.width(), bbox.height()) / 100.0) * scale_factor;
pt = detail::polylabel(polygon, bbox, precision);
return true;
}
template
bool interior(polygon<double> const& polygon, double scale_factor, point<double> & pt);
} }
Using the PriorityQueue implementation from BlackWasp:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using PriorityQueue;
namespace SkiaDemo1
{
public class PolyLabel
{
private const float EPSILON = 1E-8f;
public static float[] GetPolyLabel(float[][][] polygon, float precision = 1f)
{
//Find the bounding box of the outer ring
float minX = 0, minY = 0, maxX = 0, maxY = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon[0].Length; i++) {
float[] p = polygon[0][i];
if (i == 0 || p[0] < minX)
minX = p[0];
if (i == 0 || p[1] < minY)
minY = p[1];
if (i == 0 || p[0] > maxX)
maxX = p[0];
if (i == 0 || p[1] > maxY)
maxY = p[1];
}
float width = maxX - minX;
float height = maxY - minY;
float cellSize = Math.Min(width, height);
float h = cellSize / 2;
//A priority queue of cells in order of their "potential" (max distance to polygon)
PriorityQueue<float,Cell> cellQueue = new PriorityQueue<float, Cell>();
if (FloatEquals(cellSize, 0))
return new[] { minX, minY };
//Cover polygon with initial cells
for (float x = minX; x < maxX; x += cellSize) {
for (float y = minY; y < maxY; y += cellSize) {
Cell cell = new Cell(x + h, y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell.Max, cell);
}
}
//Take centroid as the first best guess
Cell bestCell = GetCentroidCell(polygon);
//Special case for rectangular polygons
Cell bboxCell = new Cell(minX + width / 2, minY + height / 2, 0, polygon);
if (bboxCell.D > bestCell.D)
bestCell = bboxCell;
int numProbes = cellQueue.Count;
while (cellQueue.Count > 0) {
//Pick the most promising cell from the queue
Cell cell = cellQueue.Dequeue();
//Update the best cell if we found a better one
if (cell.D > bestCell.D) {
bestCell = cell;
}
//Do not drill down further if there's no chance of a better solution
if (cell.Max - bestCell.D <= precision)
continue;
//Split the cell into four cells
h = cell.H / 2;
Cell cell1 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell1.Max, cell1);
Cell cell2 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell2.Max, cell2);
Cell cell3 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell3.Max, cell3);
Cell cell4 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell4.Max, cell4);
numProbes += 4;
}
return (new[] { bestCell.X, bestCell.Y });
}
//Signed distance from point to polygon outline (negative if point is outside)
private static float PointToPolygonDist(float x, float y, float[][][] polygon)
{
bool inside = false;
float minDistSq = float.PositiveInfinity;
for (int k = 0; k < polygon.Length; k++) {
float[][] ring = polygon[k];
for (int i = 0, len = ring.Length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
float[] a = ring[i];
float[] b = ring[j];
if ((a[1] > y != b[1] > y) && (x < (b[0] - a[0]) * (y - a[1]) / (b[1] - a[1]) + a[0]))
inside = !inside;
minDistSq = Math.Min(minDistSq, GetSegDistSq(x, y, a, b));
}
}
return ((inside ? 1 : -1) * (float)Math.Sqrt(minDistSq));
}
//Get squared distance from a point to a segment
private static float GetSegDistSq(float px, float py, float[] a, float[] b)
{
float x = a[0];
float y = a[1];
float dx = b[0] - x;
float dy = b[1] - y;
if (!FloatEquals(dx, 0) || !FloatEquals(dy, 0)) {
float t = ((px - x) * dx + (py - y) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (t > 1) {
x = b[0];
y = b[1];
} else if (t > 0) {
x += dx * t;
y += dy * t;
}
}
dx = px - x;
dy = py - y;
return (dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
//Get polygon centroid
private static Cell GetCentroidCell(float[][][] polygon)
{
float area = 0;
float x = 0;
float y = 0;
float[][] ring = polygon[0];
for (int i = 0, len = ring.Length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
float[] a = ring[i];
float[] b = ring[j];
float f = a[0] * b[1] - b[0] * a[1];
x += (a[0] + b[0]) * f;
y += (a[1] + b[1]) * f;
area += f * 3; // f * 2 では?
}
if (FloatEquals(area, 0))
return (new Cell(ring[0][0], ring[0][1], 0, polygon));
return (new Cell(x / area, y / area, 0, polygon));
}
private static bool FloatEquals(float a, float b)
{
return (Math.Abs(a - b) < EPSILON);
}
private class Cell
{
public float X { get; private set; }
public float Y { get; private set; }
public float H { get; private set; }
public float D { get; private set; }
public float Max { get; private set; }
public Cell(float x, float y, float h, float[][][] polygon)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
H = h;
D = PointToPolygonDist(X, Y, polygon);
Max = D + H * (float)Math.Sqrt(2);
}
}
}
}
polylabelのC# implementationをほぼそのまま使うことにする。
下の繰り返し計算の変数 x, y だけ double 型に変更した。 float型では精度不足で、cellSize を足しても値が増えない。
//Cover polygon with initial cells
for (double x = minX; x < maxX; x += cellSize) {
for (double y = minY; y < maxY; y += cellSize) {
Cell cell = new Cell((float)(x + h), (float)(y + h), h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell.Max, cell);
}
}
c:\gis3>converter kanto node数=37790131(タグあり 675910) BF=12 max id=2251c296f max block=2249154(2251C2) 2分13秒経過 way数=5891777 12分40秒経過 relation数=28307 way member数=209853 12分40秒経過 19572408 21090776 c:\gis3>converter japan node数=210429909(タグあり 2367745) BF=12 max id=2250415a0 max block=2248769(225041) 13分28秒経過 way数=27923762 1時間14分26秒経過 relation数=126542 way member数=752273 1時間14分29秒経過 90233379 101419530
Mapnik はポリゴンの辺への距離だけでなく、重心との距離も加味して、なるべく重心に近づけようとしている。 全般的には、この効果が見られるが、下図の場合、差がない。
公園とグランドは似た形状であるが、グランドはほぼ中心となっているのに対して、公園は上にかたよっている。 Mapnikでも改善が見られない。 念のため、チェックしたが、point データではなく、polygon の中心位置を求めたものである。
このような例は他にもある。Mapnikの方法では改善されない。
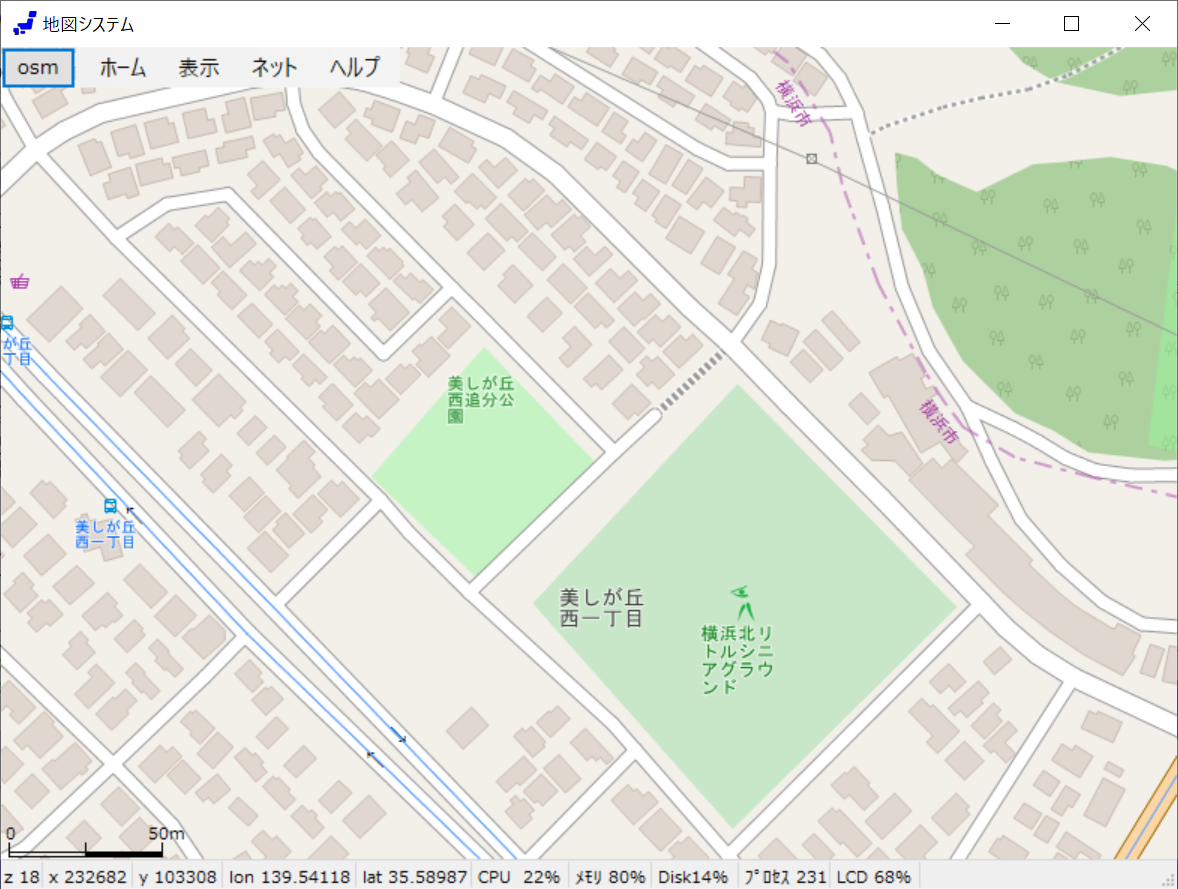
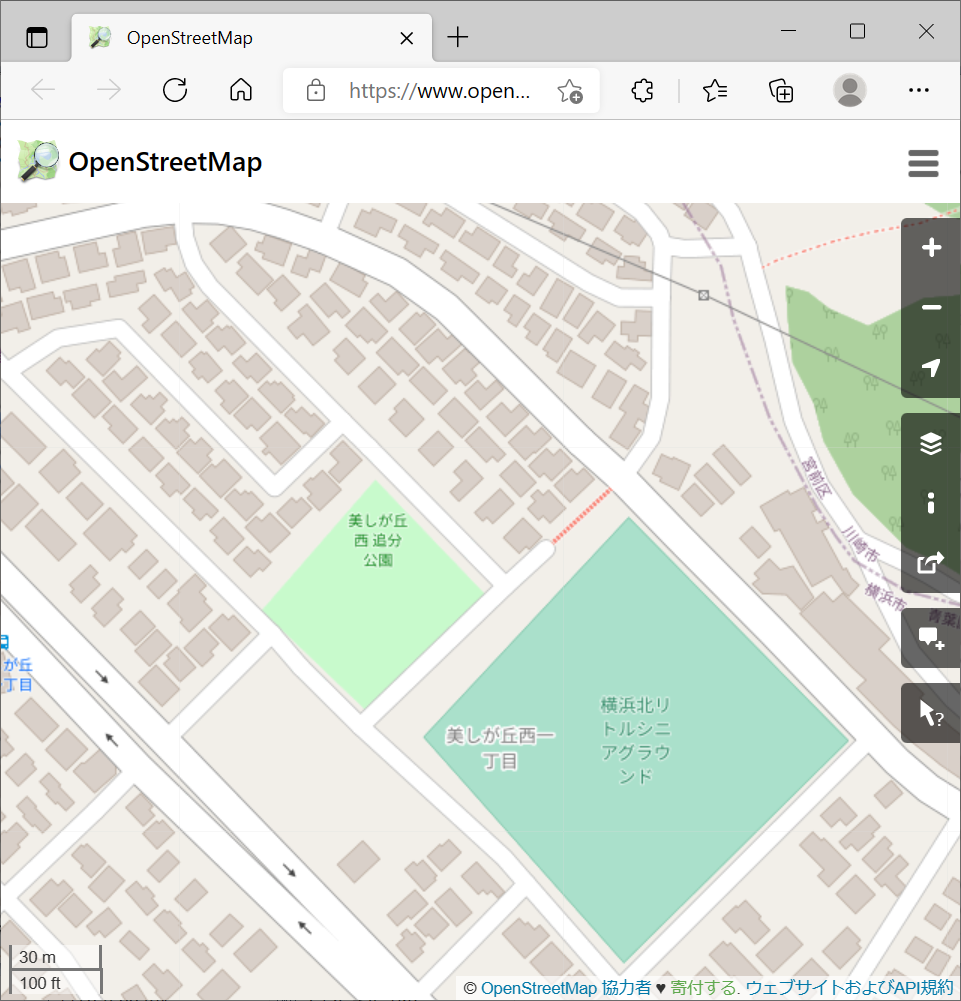
Mapnikの場合、多分、極座標と思うが確信はない。 重心に近いものを優先するために、距離を重心との距離で補正していることは確かである。 この考え方を取り入れた。
中心(center, 代表点)を必要とするようなポリゴンでは重心(centroid)も求めるようにした。 ただし、nameタグのない building=* では、中心座標は要らないので算出していない。 これにより、実行時間は1時間強となった。
1h2m52s経過 Low: 710923 824753 重複率 16% Mid: 12666657 15124478 重複率 19% High: 16978791 20422445 重複率 20% Low[7]: 193574786/710923=272, Mid[10]: 768661032/12666657=60, High[13]: 872134704/16978791=51
//Get polygon centroid
public static Node GetCentroid(Node[] poly) {
double area = 0, x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0, len = poly.Length, j = len - 1; i < len; j = i++) {
Node a = poly[i];
Node b = poly[j];
double f = (double)a.x * b.y - (double)b.x * a.y;
x += (a.x + b.x) * f;
y += (a.y + b.y) * f;
area += f * 2;
}
if (area == 0) return poly[0];
return new Node((int)(x/area), (int)(y/area));
}
PointToPolygonDistの結果(距離)を補正して、なるべく重心に近づけようとするものである。 Mapnikのプログラムを真似たものであり、結果は改善されるが、Mapnikの結果とはかなり差異がある。 一般には、Mapnikの結果の方が重心により近い。 しかし、Mapnikよりも下のプログラムの方がより良い結果となるケースもある。 例えば、前に上げた公園は下図のようになり、Mapnikよりもいい結果が得られている。
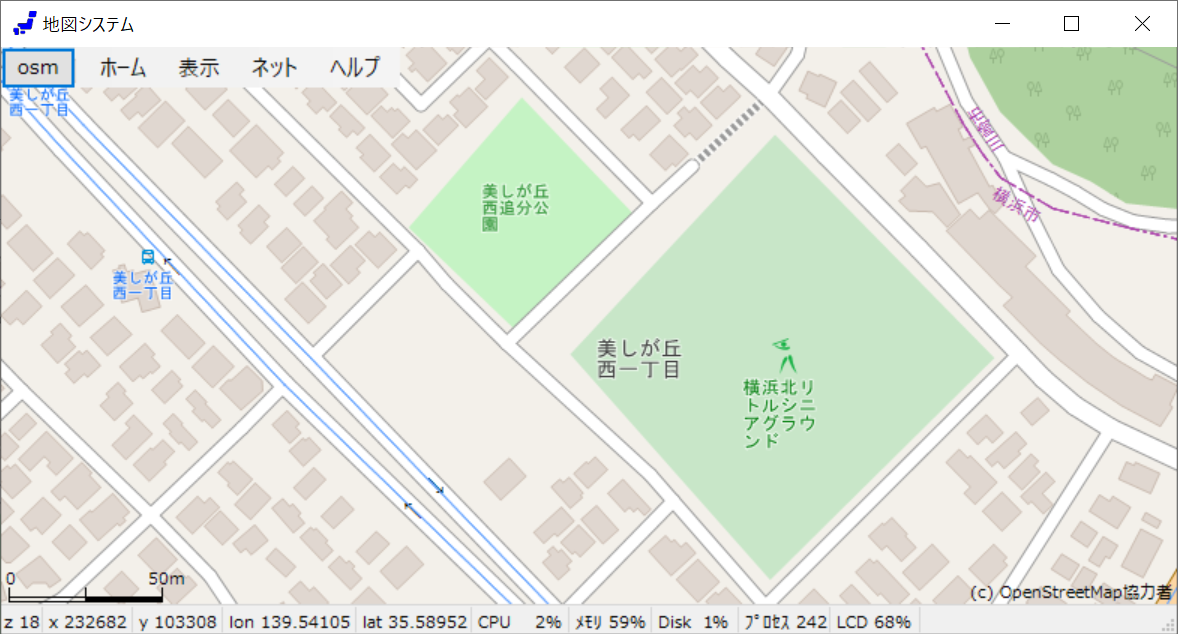
なお、 max_size = Math.Max(width, height); では、 && distance_centroid < max_size はいらないが これ以外でも試行錯誤したことから、念のために残している。
OSMデータの極座標の精度は小数点以下7桁であることから、EPISILON はこれに合わせた。 precision は Mapnik の場合 1% としているが、実行時間を短縮するため 3% にした。 EPISILON や precision が小さいほど実行時間が長くなる。
class Center {
//private const float EPSILON = 1E-8f;
private const float EPSILON = 1E-7f;
static Cell centroid;
static float max_size;
private class Cell {
public float X, Y, H, D, Max;
public Cell(float x, float y, float h, float[][][] polygon) {
X = x;
Y = y;
H = h;
D = PointToPolygonDist(X, Y, polygon);
if (centroid != null) {
double dx = X - centroid.X;
double dy = Y - centroid.Y;
double distance_centroid = Math.Sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (D > 0 && distance_centroid < max_size)
D = (float)(D * (1 - distance_centroid / max_size));
}
Max = D + H * (float)Math.Sqrt(2);
}
}
public static float[] GetCenter(float[][][] polygon, float[] centro) {
//Find the bounding box of the outer ring
float minX = float.MaxValue, minY = float.MaxValue;
float maxX = float.MinValue, maxY = float.MinValue;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon[0].Length; i++) {
float[] p = polygon[0][i];
if (p[0] < minX) minX = p[0];
if (p[1] < minY) minY = p[1];
if (p[0] > maxX) maxX = p[0];
if (p[1] > maxY) maxY = p[1];
}
float width = maxX - minX;
float height = maxY - minY;
float cellSize = Math.Min(width, height);
float h = cellSize / 2;
max_size = Math.Max(width, height);
float precision = cellSize * 3.0f / 100.0f; // 3%. 2021.11.30
//A priority queue of cells in order of their "potential" (max distance to polygon)
PriorityQueue<float,Cell> cellQueue = new PriorityQueue<float, Cell>();
if (FloatEquals(cellSize, 0))
return new[] { minX, minY };
//Take centroid as the first best guess
centroid = new Cell(centro[0], centro[1], h, polygon);
Cell bestCell = centroid;
//Cover polygon with initial cells
for (double x = minX; x < maxX; x += cellSize) {
for (double y = minY; y < maxY; y += cellSize) {
Cell cell = new Cell((float)(x + h), (float)(y + h), h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell.Max, cell);
}
}
//Special case for rectangular polygons
Cell bboxCell = new Cell(minX + width/2, minY + height/2, 0, polygon);
if (bboxCell.D > bestCell.D)
bestCell = bboxCell;
int numProbes = cellQueue.Count;
while (cellQueue.Count > 0) {
//Pick the most promising cell from the queue
Cell cell = cellQueue.Dequeue();
//Update the best cell if we found a better one
if (cell.D > bestCell.D) {
bestCell = cell;
}
//Do not drill down further if there's no chance of a better solution
if (cell.Max - bestCell.D <= precision)
continue;
//Split the cell into four cells
h = cell.H / 2;
Cell cell1 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell1.Max, cell1);
Cell cell2 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y - h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell2.Max, cell2);
Cell cell3 = new Cell(cell.X - h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell3.Max, cell3);
Cell cell4 = new Cell(cell.X + h, cell.Y + h, h, polygon);
cellQueue.Enqueue(cell4.Max, cell4);
numProbes += 4;
}
return (new[] { bestCell.X, bestCell.Y });
}